What is Medical Triage?
Medical triage is the process of prioritizing patients based on the severity of their injuries or illnesses. This system ensures that people with the most critical needs receive immediate attention, especially in emergency situations like accidents, disasters, or on the battlefield.
The goal of triage is simple: to save lives by treating those who need urgent care first. It’s an essential process in situations where medical resources are limited and patients are numerous.
Why Is It Called Triage?
The term “triage” comes from the French word trier, meaning “to sort.” It dates back to the days of Napoleon when doctors needed a way to sort soldiers based on the severity of their wounds. Over time, triage systems have been refined and are now used globally in hospitals, emergency response teams, and disaster scenarios.
How Does Medical Triage Work?
Triage systems may vary slightly depending on the organization, but they all have the same goal: to prioritize treatment based on the severity of a patient’s condition. One of the most common systems uses color-coded categories to quickly assess who needs immediate care and who can wait.
Here’s a breakdown of these categories:
- Red: Immediate, life-threatening injuries or conditions that require urgent treatment.
- Yellow: Serious injuries that need attention but are not immediately life-threatening.
- Green: Minor injuries that are non-life-threatening and can be treated later.
- Black: Deceased or critically injured patients who cannot be saved.
- White: No injuries or medical conditions.
This classification helps healthcare providers quickly decide who gets treated first and ensures the most critical cases are handled immediately.
The Triage Process: Before and After the Hospital
Before the Hospital (Emergency Medical Services)
When emergency medical technicians (EMTs) arrive at the scene of an accident or disaster, their first task is to assess patients based on their injuries, vital signs, and mental status. Patients with life-threatening injuries (classified as “red”) are transported to the nearest trauma center first.
For patients with serious but less critical conditions (classified as “yellow”), treatment is needed, but they can wait longer. Other patients with minor injuries (classified as “green”) may not need to be transported right away.
In the Hospital (Emergency Department)
Upon arrival at the hospital, patients undergo a second round of triage in the emergency department (ED). In most U.S. hospitals, the Emergency Severity Index (ESI) is used to sort patients into five levels of urgency:
- Level I: Most urgent, requiring immediate life-saving interventions.
- Level II: Serious, but not immediately life-threatening.
- Level III: Moderate conditions that can be treated soon.
- Level IV: Minor issues that do not require urgent care.
- Level V: Non-urgent cases.
This system helps ensure that patients are treated based on the severity of their condition, not just the order in which they arrive.
When Is Medical Triage Used?
Triage is used whenever there are more patients than resources to treat them. It helps healthcare providers decide who gets care first. Triage is especially crucial in the following scenarios:
- Emergency Rooms (ERs): During peak hours or in crisis situations when the ER is overcrowded, triage ensures that the most critical patients are seen first.
- Mass Casualty Events: Disasters, accidents, or terrorist attacks can overwhelm hospitals and emergency services. Triage is used to prioritize the most seriously injured.
- Military Triage: On the battlefield, soldiers are triaged to determine who should be treated first based on the severity of their injuries.
In all these situations, the goal of triage is to use available resources efficiently and save as many lives as possible.
Types of Triage
Different situations require different types of triage:
- Emergency Department Triage: Used in hospitals to sort patients as they arrive at the emergency room.
- Incident (Multicasualty) Triage: Used when multiple people are injured, such as in a car accident.
- Disaster (Mass Casualty) Triage: This is for large-scale emergencies, such as natural disasters or terrorist attacks. The START system is often used to triage patients quickly.
- Military Triage: Used to assess and treat wounded soldiers on the battlefield.
- Telephone Triage: Nurses assess symptoms over the phone to decide whether patients need immediate care or can wait for an in-person visit.
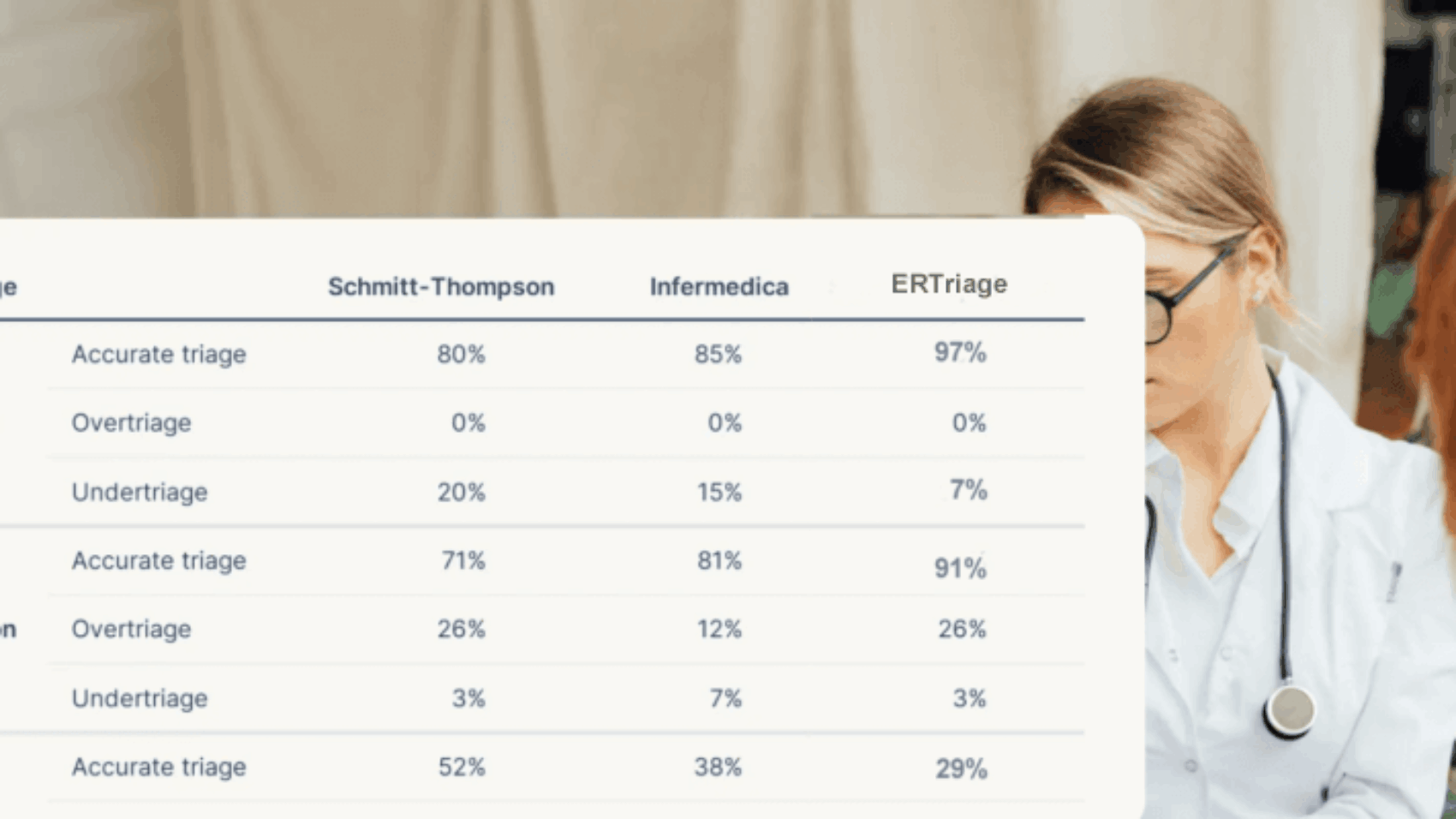
How Technology is Changing Triage
Advancements in technology are significantly improving how triage is conducted. Telemedicine, for example, allows healthcare professionals in remote areas to consult with trauma specialists in real-time. This helps ensure that patients in rural or underserved areas receive timely care.
Another technological advancement is artificial intelligence (AI). Traditional triage involves subjective decision-making, but AI can analyze patient data and make more objective, faster decisions. For example, AI tools can assess a patient’s condition based on their medical history and symptoms, recommending the appropriate triage level.
Some hospitals in the U.S. have already started using AI-based triage systems to improve accuracy and efficiency. This technology not only speeds up the triage process but also helps healthcare providers make more informed decisions.
Summary
Medical triage is a vital process used to prioritize patients in emergencies. By sorting patients based on the severity of their injuries or illnesses, triage helps ensure that those who need urgent care are treated first. It’s commonly used in emergency rooms, mass casualty events, and military situations.
Triage systems vary but typically use color-coding or a numerical system to rank the urgency of care. As technology advances, tools like telemedicine and artificial intelligence are improving the accuracy and speed of triage, making healthcare more efficient and accessible.
By understanding and implementing triage effectively, healthcare professionals can make the most of available resources and save more lives in critical situations.