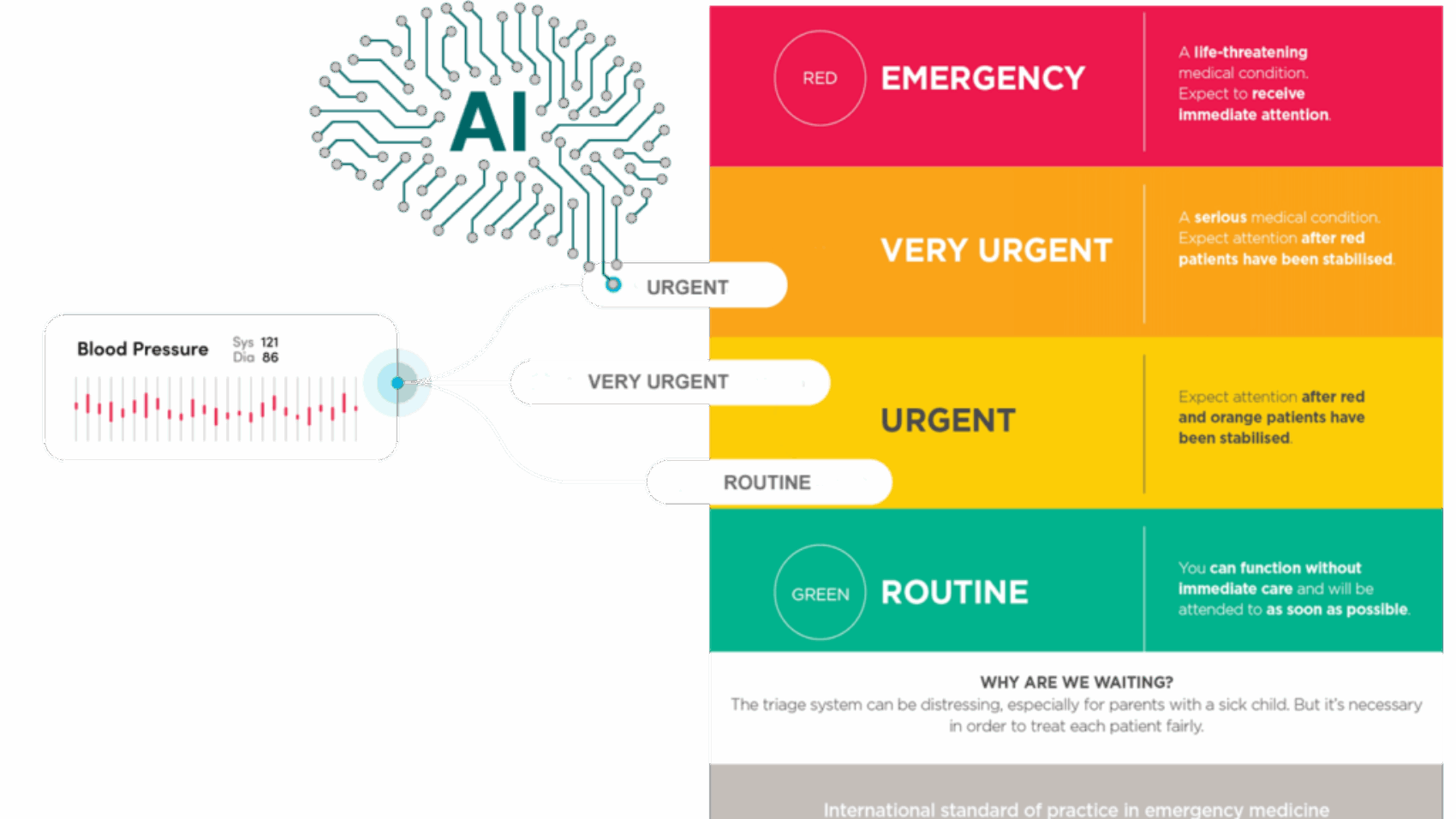
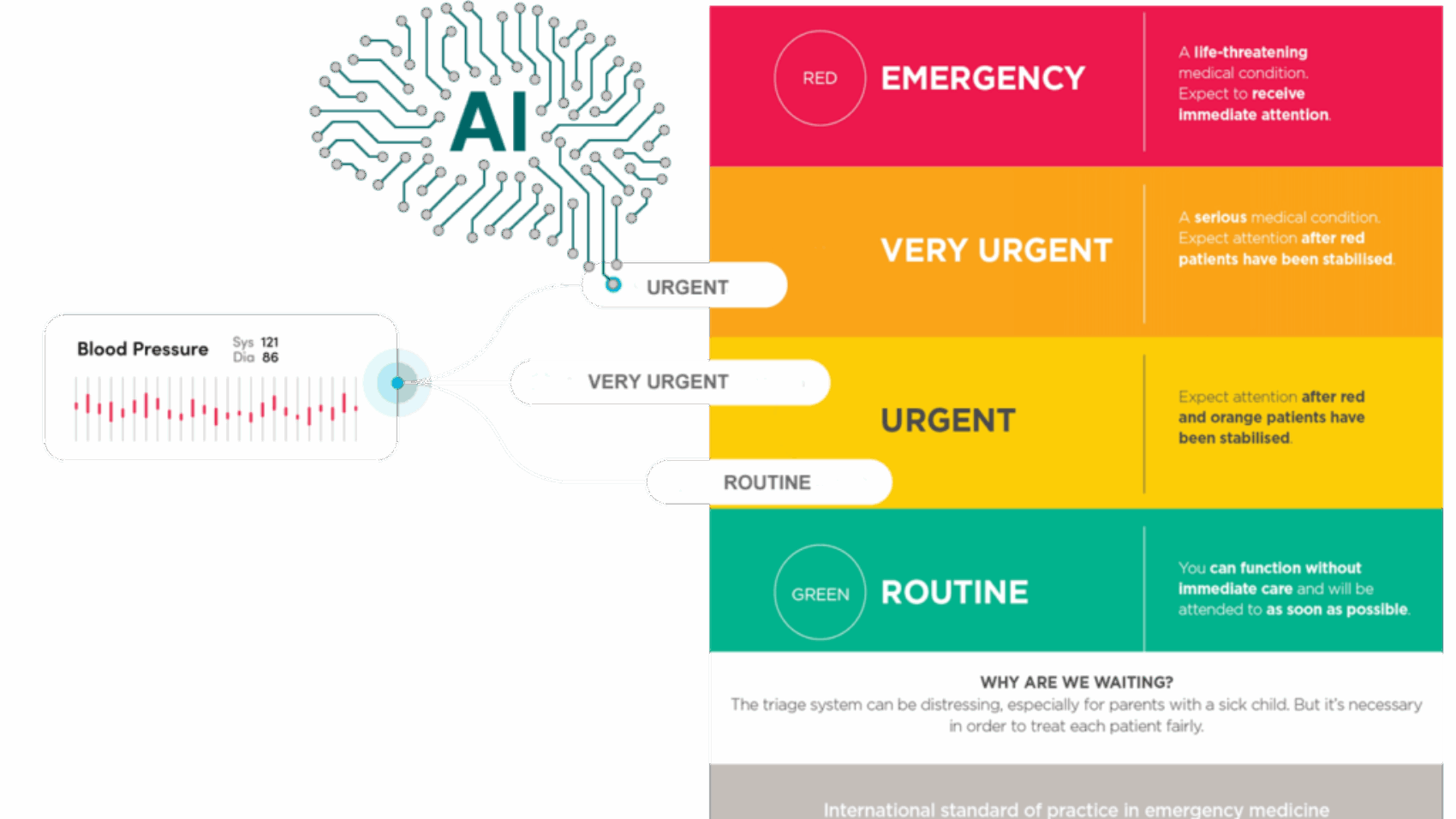
In the event of a mass casualty incident (MCI), where numerous individuals suffer serious injuries or life-threatening conditions, triage becomes an essential part of the medical response. The goal of triage is to determine which patients need immediate care and which can wait. Traditionally, this process has relied on the expertise and judgment of healthcare professionals. However, the increasing number of patients and pressure on healthcare systems can make traditional methods slow and prone to errors. Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers a solution to streamline triage, improving speed, accuracy, and efficiency. This article explores how AI can transform triage practices, benefiting both healthcare professionals and patients.
AI’s Role in Triage During Mass Casualty Incidents
MCIs, whether caused by natural disasters, terrorist attacks, or large-scale accidents, can overwhelm healthcare services. In such high-pressure environments, healthcare workers must make fast decisions about which patients receive priority care. AI can enhance triage by reducing assessment time, providing better predictions of patient outcomes, and optimizing the use of limited medical resources. Here’s how AI can improve triage during MCIs:
1. Rapid Patient Assessment with AI
In MCIs, the speed of patient assessment directly impacts survival chances. AI can accelerate this process by analyzing patient data quickly and accurately. Traditional triage involves manually assessing patients based on vital signs, symptoms, and physical examinations, which can be slow when large numbers of patients require attention.
AI-powered systems automate data collection by integrating information from sources like vital signs, medical history, and wearable devices. Machine learning algorithms can instantly analyze these data points to assess the severity of a patient’s condition. For example, if a patient presents with shortness of breath, AI can analyze their oxygen levels, respiratory rate, and heart rate to identify life-threatening conditions like respiratory failure or shock, allowing healthcare workers to prioritize those needing urgent care.
2. Predicting Patient Outcomes
AI can also predict patient outcomes, which is crucial for triage. Healthcare professionals often rely on clinical experience to estimate prognosis, but these predictions can be inaccurate. AI, however, can analyze large datasets of patient information—including historical health data and injury severity—to predict recovery or survival chances.
For instance, AI can assess whether a patient’s injuries might lead to organ failure or whether they are at risk of complications like infections. These insights allow healthcare professionals to make data-driven decisions, helping to prioritize immediate interventions such as surgery or intensive care.
3. Optimizing Resource Allocation with AI
In an MCI, healthcare resources such as hospital beds, ventilators, and medical staff are often in limited supply. AI helps optimize these resources to ensure they are allocated where most needed. Real-time tracking of resources allows AI systems to suggest the most efficient distribution based on patient requirements.
For example, if ventilators are in short supply, AI can prioritize which patients should receive mechanical ventilation based on their condition. AI can also track the availability of healthcare professionals and direct them to the most critical cases, ensuring that resources are used effectively and efficiently.
4. Real-Time Monitoring of Medical Equipment and Resources
AI can monitor the availability of necessary medical equipment such as blood transfusion bags or surgical tools. By providing real-time updates, AI helps healthcare workers make informed decisions about resource allocation, ensuring that limited resources are used where they are needed most.
Integrating AI with Traditional Triage Protocols
While AI offers many benefits, it should complement, not replace, human judgment in triage. For AI to be effective, it must integrate seamlessly with traditional triage protocols. Here’s how:
1. Training Healthcare Workers to Use AI Tools
Healthcare workers must be trained to use AI tools effectively. AI systems should assist rather than take over decision-making. Medical staff should learn how to interpret AI assessments and integrate them with their clinical expertise. Regular updates to AI algorithms will ensure they remain accurate and relevant as medical practices evolve.
2. Addressing Ethical Concerns
AI in triage raises ethical concerns, particularly regarding patient privacy and transparency. Patient data, including medical histories and personal information, must be protected. Robust data security measures must be implemented to safeguard patient information.
Transparency is crucial in ensuring patient trust. Patients must understand how AI is being used in their care and that final decisions are made by healthcare professionals. Clear communication about AI’s role in triage will help build trust and ensure its successful integration.
The Future of AI in Triage Systems
Looking ahead, AI is set to play an even more significant role in triage systems, particularly during MCIs. As AI technology advances, triage systems will become faster, more accurate, and capable of handling larger volumes of data. These systems will not only improve triage but also help healthcare systems become more responsive and efficient in emergencies.
In the future, we may see fully automated triage systems for initial patient assessments. However, these systems must remain tools that support healthcare professionals rather than replace them. A balance between AI and human decision-making will ensure patients receive the highest quality of care, even in the most challenging circumstances.
Conclusion
AI has the potential to revolutionize triage practices during mass casualty incidents. By enhancing patient assessment speed, predicting outcomes, and optimizing resource allocation, AI can significantly improve the response to emergencies. When integrated with traditional triage protocols, AI can provide healthcare professionals with valuable insights, helping them make faster, more accurate decisions. As AI technology continues to evolve, its role in triage will expand, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective healthcare responses in mass casualty situations.